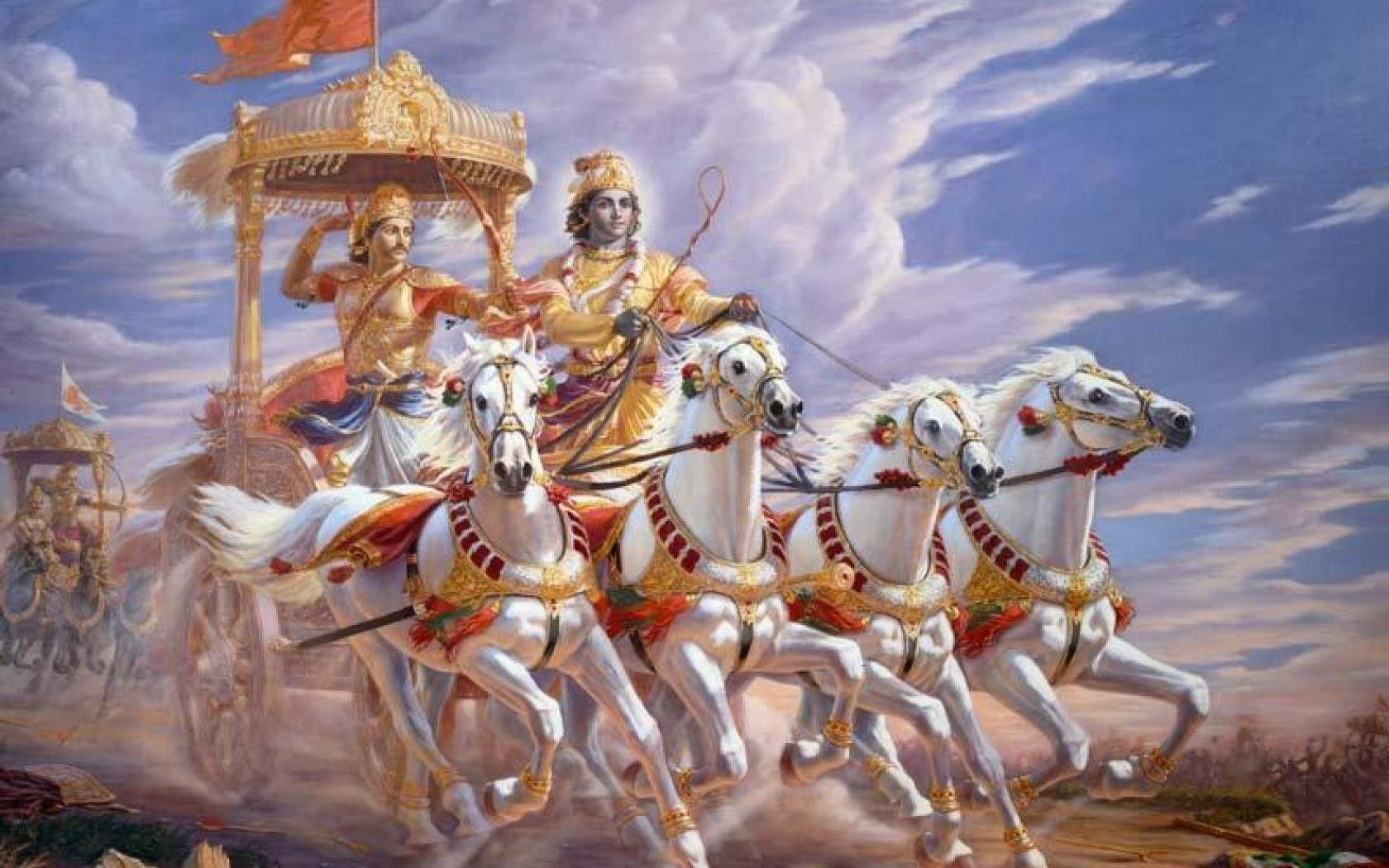
The Bhagavad Gītā, often referred to simply as the Gita, is a 700-verse Hindu scripture that is part of the Indian epic Mahabharata. It is the sacred text of great spiritual and philosophical significance. It is a conversation taking place on the battlefield of Kurukshetra, between the mighty warrior Arjuna and Lord Krishna (who serves as his charioteer).
The Gita's teachings emphasize the importance of fulfilling one's responsibilities and duties while maintaining inner peace and detachment from the results of actions. It provides insights into the nature of the self, the concept of dharma (duty) and the eternal truth that transcends the material world.
The Bhagavad Gita has had a profound influence on philosophy, ethics, and spirituality not only in India but also around the world. Its universal themes continue to inspire individuals on their spiritual journeys and guide them towards a deeper understanding of life's purpose.
At its core, the Bhagavad Gita addresses profound questions about life, duty, righteousness, and the path to spiritual realisation. It explores four primary yogas (path) to spiritual growth, each offering a unique approach to spiritual realisation and self-discovery. These four yogas are:
Bhakti Yoga (the yoga of devotion)
Bhakti Yoga is the path of devotion and love for the Divine. It involves surrendering to a personal deity, developing a deep emotional connection and serving the Divine with unwavering faith and devotion. Love and devotion are seen as powerful means of attaining spiritual realisation.
Karma Yoga (the yoga of selfless action)
This path emphasises selfless action and performing one's duties without attachment to the results. It teaches that dedicating all actions to the Divine, without selfish desires, purifies the mind and leads to spiritual growth.
Jñāna Yoga (the yoga of knowledge)
Jñāna Yoga is the yoga of knowledge and wisdom. It involves deep contemplation, self-inquiry and the pursuit of self-realization through understanding the nature of the self (Atman) and its relationship to the ultimate reality (Brahman). It explores profound philosophical concepts to gain insight into the nature of existence.
Dhyāna Yoga (the yoga of meditation)
This path is often associated with meditation and the control of the mind. It teaches techniques for quieting the mind, focusing inward, and attaining a state of deep meditation. Through disciplined practice, individuals aim to directly experience the Divine within.
The Bhagavad Gita presents these paths as complementary, recognising that individuals may resonate with one or more of these approaches to spiritual growth. It emphasises the importance of choosing a path that aligns with one's nature and inclinations while ultimately leading to the realisation of the same spiritual truth.
Its teachings transcend time and culture, offering profound insights into the human condition and the pursuit of spiritual growth.
This sacred scripture is a treasure trove of philosophical and spiritual wisdom and has had a profound influence on mankind. It continues to be a source of inspiration and guidance for those on the path of self-realisation and spiritual awakening.
Glossary
Gītā - Geetaa
Jñāna - Gyaana
Dhyāna - Dhyaana